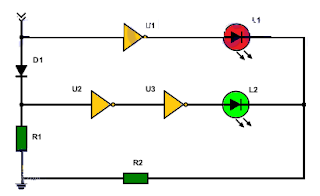
This simple logic tip with inverters is implemented with three NOT (NO) gates, one rectifier diode, two LEDs and two resistors. The tip or logical probe allows to determine the logical state of any point in a digital circuit. The signal is applied to the IN input.
This tip is very easy to construct, because it uses few elements that could easily be located on a very narrow printed circuit board (PCB). Such a plate could be placed without problems in a thick tube or pencil in disuse.
Operation of the logical tip with inverters
If the signal being measured is a "high" logic level:
If the signal being measured is a "low" logic level:
Resistor R2 limits the current flowing through the LEDs (green and red)
To implement the circuit you need an integrated circuit TTL (Transistor Transistor Logic) SN7404 with 6 NOT gates. Keep in mind that the voltage source that will power this circuit is 5 volts and can only be used to test digital circuits manufactured with TTL integrated circuits.
Take into account that the ground connection (0 volts) of the circuit under test and the 0V terminal of the logic tip must be the same.
Note: There are three integrated NOT gates that are not used in circuit operation. They should put their inputs at 5 volts (logical level "high").
List of tip components / logical shadow
1 TTL integrated circuit SN7404 (6 inverters / NOT gates). Only 3 (U1, U2, U3) are used
1 rectifier diode 1N4001 or similar (D1)
2 common LEDs (red, green) (L1, L2)
1 resistor of 220 ohms, 1/4 watt (R2)
1 resistance of 10K, 1/4 watt (R1)
This tip is very easy to construct, because it uses few elements that could easily be located on a very narrow printed circuit board (PCB). Such a plate could be placed without problems in a thick tube or pencil in disuse.
Operation of the logical tip with inverters
If the signal being measured is a "high" logic level:
- The upper inverter inverts the signal (logic level "low") and the red LED does not turn on.
- The common diode is polarized live. The signal is inverted twice by the two inverters in cascade and the green LED lights up (logic level "high").
If the signal being measured is a "low" logic level:
- The upper inverter inverts the signal and the red LED turns on (logic level "high").
- The common diode does not drive. As a consequence there is a "low" logic level at the anode of the diode. This low level is reversed twice by the inverters in cascade and the green LED does not turn on (logic level "low").
Resistor R2 limits the current flowing through the LEDs (green and red)
To implement the circuit you need an integrated circuit TTL (Transistor Transistor Logic) SN7404 with 6 NOT gates. Keep in mind that the voltage source that will power this circuit is 5 volts and can only be used to test digital circuits manufactured with TTL integrated circuits.
Take into account that the ground connection (0 volts) of the circuit under test and the 0V terminal of the logic tip must be the same.
Note: There are three integrated NOT gates that are not used in circuit operation. They should put their inputs at 5 volts (logical level "high").
List of tip components / logical shadow
1 TTL integrated circuit SN7404 (6 inverters / NOT gates). Only 3 (U1, U2, U3) are used
1 rectifier diode 1N4001 or similar (D1)
2 common LEDs (red, green) (L1, L2)
1 resistor of 220 ohms, 1/4 watt (R2)
1 resistance of 10K, 1/4 watt (R1)











0 comments:
Post a Comment